近日,我校地理与环境科学学院魏伟副教授团队在国际遥感科学领域顶级期刊《Remote Sensing of Environment》在线发表了题为“Temperature Vegetation Precipitation Dryness Index (TVPDI)-based dryness-wetness monitoring in China”的学术论文。
该成果从降水、土壤水分和地表植被响应等方面入手,全面梳理和总结主要致旱因子及其遥感监测机理,重建了中国陆地2001-2017年1月至12月的干旱时空分布和干旱等级情况,对模型计算所得干湿状况的准确性和科学性等方面进行了验证,并利用Landsat计算结果进行了对比。该研究成果提出的方法和技术可从大尺度、长时间序列科学评价地区综合干旱情况和干旱发生等级,对当地农业生产和防旱抗旱综合措施制定具有重要指导意义。
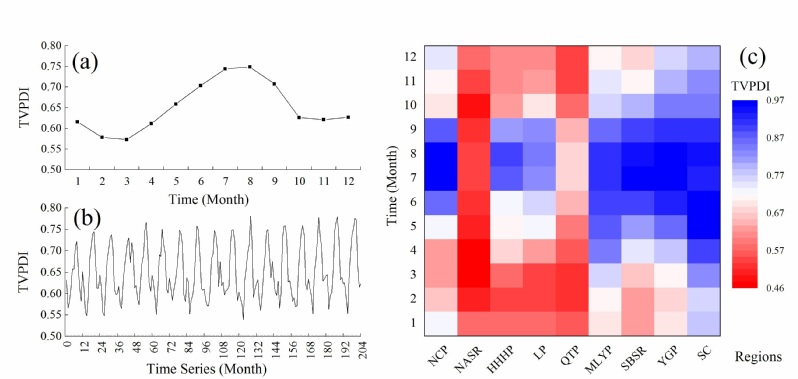
Fig. 1 Monthly variation in the TVPDI values for (a) 12 months, (b) 204 months, and (c) agricultural regions.
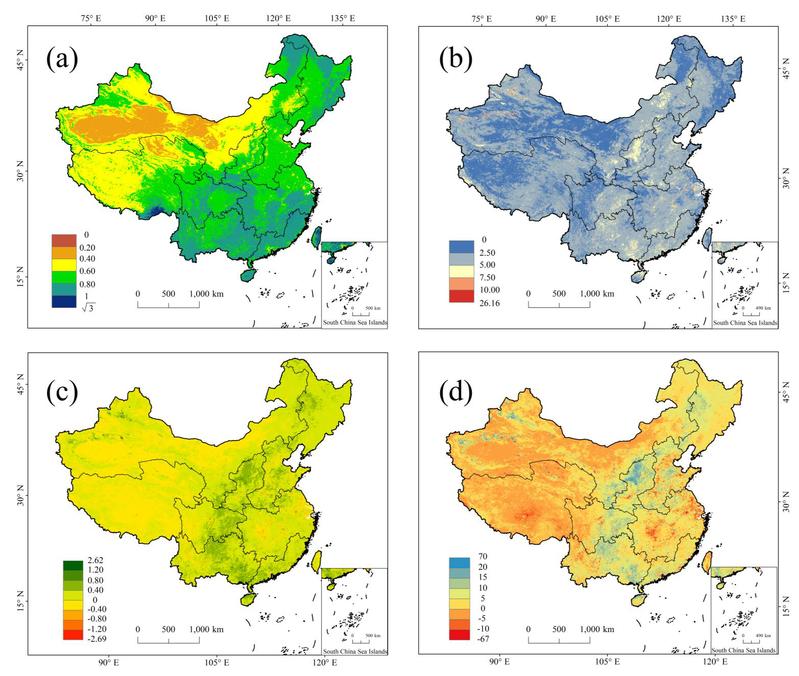
Fig. 2. The spatial distribution of (a) the multiyear average TVPDI value (1 km×1 km), (b) TVPDICV (1 km×1 km), (c) TVPDIslope (1 km×1 km) and (d) TVPDIpercentage change (1 km×1 km). The TVPDICV and TVPDIslope value in the map is the result of the origin value multiplied by 100.
Wei Wei,Sufei Pang ,Xufeng Wang,Liang Zhou,Binbin Xie,Junju Zhou,Chuanhua Li. Temperature Vegetation Precipitation Dryness Index (TVPDI)-based dryness-wetness monitoring in China[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2020, 248:111957.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2020.111957
成果链接:https://authors.elsevier.com/c/1bKMA7qzSr6wk
